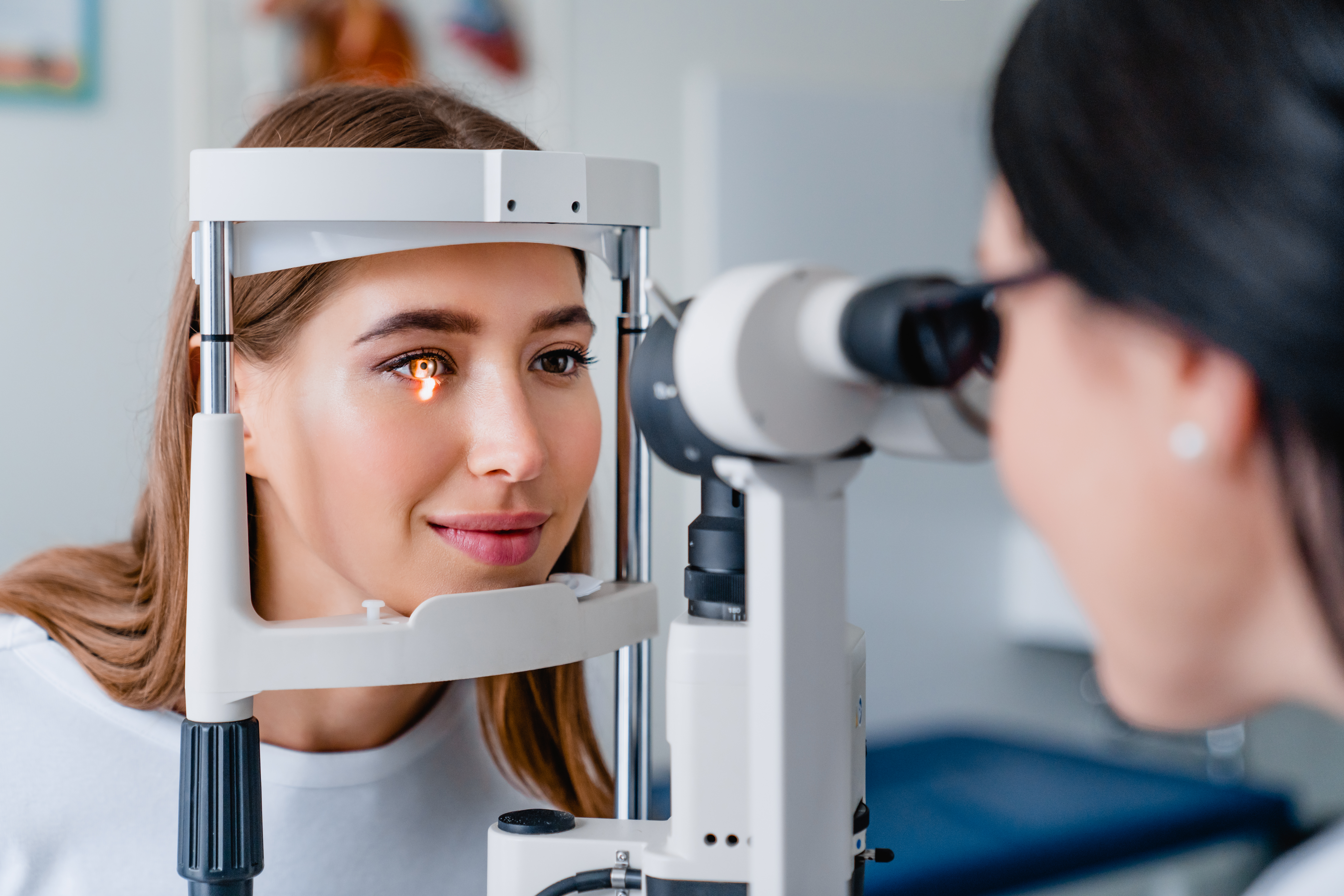
Retinal Detachment: Symptoms, Types, and Treatments
Retinal detachment, also known as retinal ablation, is an eye condition requiring immediate medical attention. Here is a detailed overview.
What is Retinal Detachment?
Retinal detachment occurs when the retina separates from the back of the eye, which consists of a layer of blood vessel cells.
The retina is a thin layer of tissue located at the back of the eyeball. Its function is to convert incoming light into electrical signals, which are then sent to the brain, allowing you to see the objects clearly.
Meanwhile, the layer of blood vessel cells provides oxygen and nutrients to the eye. Therefore, the longer the retina is detached, the greater the risk of permanent vision loss.
Symptoms of Retinal Detachment
When the retina detaches from its proper position, most people do not feel pain. However, several symptoms may appear before the retina completely detaches:
- Sudden appearance of many small floating spots.
- Photopsia, a condition where flashes of light appear in one or both eyes.
- Blurred vision.
- Gradual reduction in peripheral vision.
- A shadow appears like a curtain in your field of vision.
Visit the emergency room immediately if you experience any of these symptoms, as retinal detachment is an emergency condition. Permanent blindness can occur within a few days after symptoms appear.
Types of Retinal Detachment
The types of retinal detachment are categorized based on their causes:
1. Rhegmatogenous
This is the most common type of retinal detachment, usually influenced by aging. As one ages, the vitreous (the gel filling the eye) may change in consistency, causing it to shrink or become more liquid.
When this happens, the vitreous can peel away from the retina, potentially causing a tear. If not treated promptly, vitreous fluid can flow through the tear and accumulate behind the retina, leading to detachment.
2. Tractional
This type can occur when scar tissue grows on the retina's surface, pulling it away from the back of the eye. It usually occurs in individuals with uncontrolled diabetes.
3. Exudative
This type can result from macular degeneration (age-related vision loss), tumors, or eye inflammation, causing fluid to accumulate under the retina and eventually leading to detachment.
Risk Factors for Retinal Detachment
Several factors can increase the risk of retinal detachment, including:
- Aging, particularly over 50.
- Previous retinal detachment in one eye.
- Family history of retinal detachment.
- Severe myopia (nearsightedness).
- Previous eye surgery, such as cataract removal.
- Severe eye injury.
- Certain eye conditions such as retinoschisis (congenital splitting of the retina) and uveitis ((inflammation of the layer between the sclera and retina).
Diagnosis of Retinal Detachment
To determine if you have retinal detachment, a doctor will typically perform several tests:
- Dilated Eye Exam. Giving eye drops are used to dilate the pupil, allowing the doctor to view the retina more easily.
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT). A machine scans the eye to create detailed images.
- Fundus Imaging. The doctor takes wide-angle pictures of your retina.
- Eye Ultrasound. Local anesthetic drops are used before a CT-scan examination.
Treatment for Retinal Detachment
If diagnosed with this condition, the doctor may suggest one or more of the following treatments:
1. Laser Therapy or Cryopexy
If a retinal tear is detected early, the doctor can use laser therapy (which employs heat) or cryopexy (a freezing instrument) to seal the tear. Both methods will create scar tissue that helps the retina remain attached to its proper position.
2. Pneumatic Retinopexy
Here are the steps you will undergo during a pneumatic retinopexy procedure for retinal detachment:
- The doctor will inject a small air bubble into your eye.
- This bubble will press against the retina to help close the tear.
- If this is not fully effective, you may receive laser therapy or cryopexy (freezing) to seal the tear.
- Once the tear is sealed, your body will reabsorb the fluid that has accumulated under the retina.
- As the fluid is absorbed, the retina can reattach to the back layer of the eye.
- Eventually, the air bubble that was injected will also be absorbed by your body.
3. Scleral Buckle
This is a surgical procedure to secure the sclera (the part of the eye that helps maintain the shape of the eyeball). Here are the details of the procedure you may undergo:
- The doctor will place a silicone band or sponge (buckle) around the eye.
- This band will hold the retina in place and is permanent, so no further surgery is required to remove the buckle.
- Next, the doctor will seal any retinal tears with laser therapy or cryopexy.
- To help the retina reattach to its proper position, the doctor may inject a gas bubble or drain the fluid that has accumulated behind it.
4. Vitrectomy
This surgery removes the vitreous (the fluid that helps maintain the shape of the eye).. The procedure includes:
- Using laser or cryopexy to close tears.
- Injecting an air bubble to reattach the retina.
- If oil bubbles are used, another surgery may be required later to remove them.
Post-Surgery Care
Vision improvement is typically seen after 4-6 weeks, but full recovery may take several months. During this period, it is important to follow your doctor’s post-operative care instructions closely to ensure the best possible outcome.
- Taking pain reliever medicine as advised.
- Wearing an eyepatch.
- Keeping your head in a specific position as directed.
- Using prescribed eye drops regularly.
- Avoiding air travel until the air bubble is absorbed to prevent increased pressure in the eye.
Complications of Surgery
While retinal detachment surgery is usually successful, there are potential complications, such as:
- Bleeding.
- Infection.
- Increased intraocular pressure.
- Possible need for further surgery.
- Scar tissue formation that can cause retinopathy proliferative or epiretinal membrane.
- Rapid cataract formation requiring surgery.
Prevention of Retinal Detachment
High-risk individuals can reduce their chances of retinal detachment by:
- Having regular eye check-ups, at least annually.
- Wearing eye protection during activities that could cause eye injury.
- Consulting a doctor immediately if symptoms of retinal detachment occur.
- Maintaining stable blood pressure and blood sugar levels.
- Leading a healthy lifestyle.
For medical check-ups or treatment related to retinal detachment, Bali International Hospital (BIH) is an excellent choice.
Located in Indonesia's first Health Special Economic Zone (KEK) known as The Sanur, BIH offers comprehensive services including diagnosis, treatment, long-term care, psychological and nutritional support, and patient education programs.
Supported by professional healthcare providers, cutting-edge medical technology, world-class services, and top-tier facilities, BIH ensures a safer, more effective, and comfortable journey to health.
Related Articles
Mole surgery is a safe procedure with a relatively high success rate. What preparations are needed ...
Kidney stones (nephrolithiasis) are hard objects formed from chemicals in the kidneys. Once formed, the stone ...
Dental implants can be an excellent solution for replacing damaged or lost adult teeth. Before deciding ...

